A QMS embodies a synchronized array of principles and procedures adopted by organizations to ensure adherence to standards expected by clients and key stakeholders. The ISO 9001:2015 standard serves as the global benchmark, delineating the overarching requisites of a QMS.
A robust QMS not only aids organizations in achieving vital operational targets but also provides tangible evidence to stakeholders of their attainment.
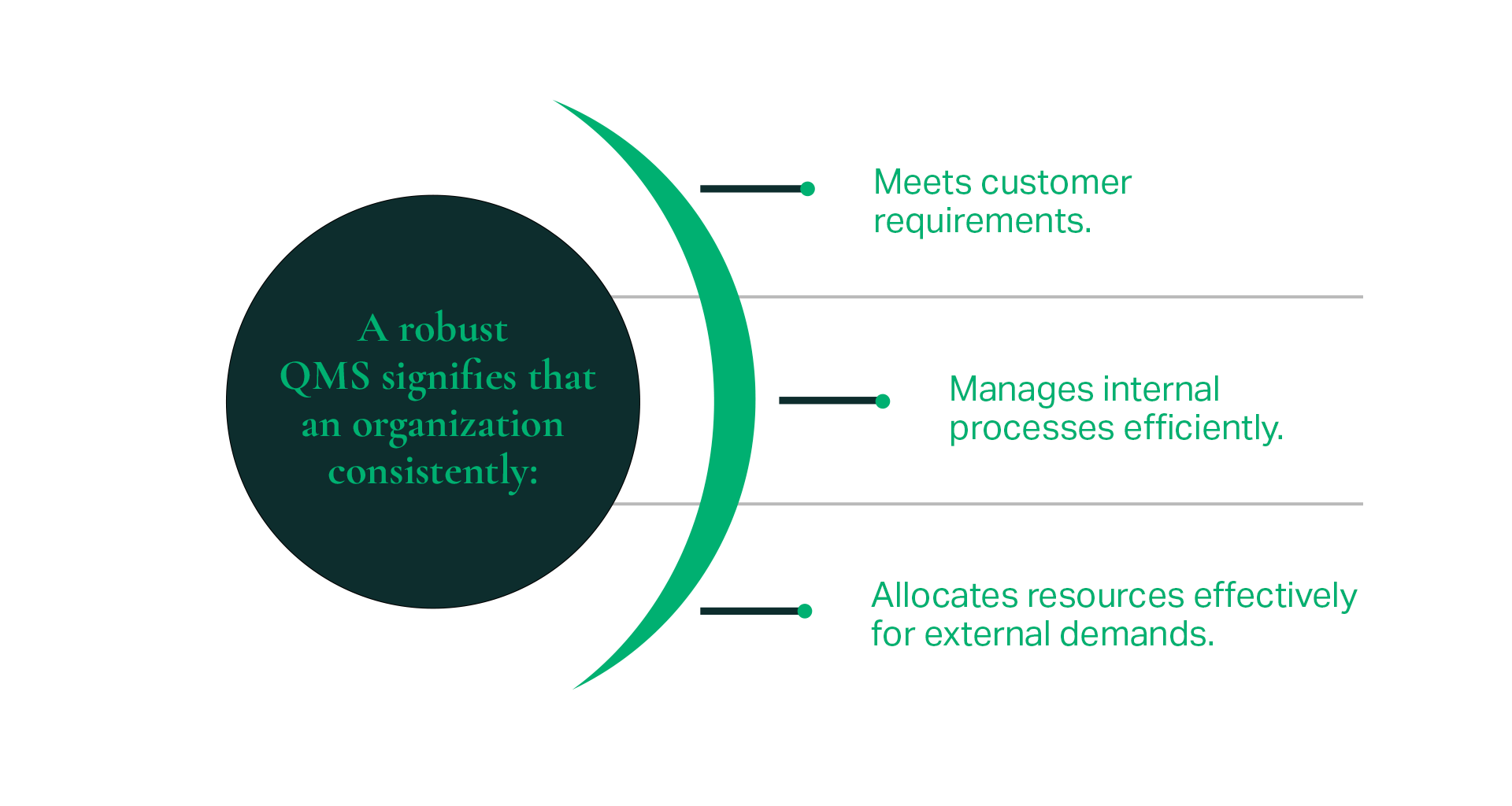 Additionally, it leads to enhanced accessibility of documentation, safeguarding of sensitive data, timely rectification of issues for perpetual enhancement of products and services, and expansion of market share into new territories and sectors. It cultivates a culture centered on quality, infuses a visionary approach into all projects, and augments internal communications. This ensures consistency in product output, effective evaluation of individual and team performance, and heightened compliance.
Additionally, it leads to enhanced accessibility of documentation, safeguarding of sensitive data, timely rectification of issues for perpetual enhancement of products and services, and expansion of market share into new territories and sectors. It cultivates a culture centered on quality, infuses a visionary approach into all projects, and augments internal communications. This ensures consistency in product output, effective evaluation of individual and team performance, and heightened compliance.
Introducing a QMS can signify a substantial shift for employees, necessitating unwavering support from operational and executive management. For maximum effectiveness, a QMS should be sturdy, intuitive, and adaptable. This may lead to shifts in staff interactions and responsibilities, requiring judicious management of employee attitudes and concerns.
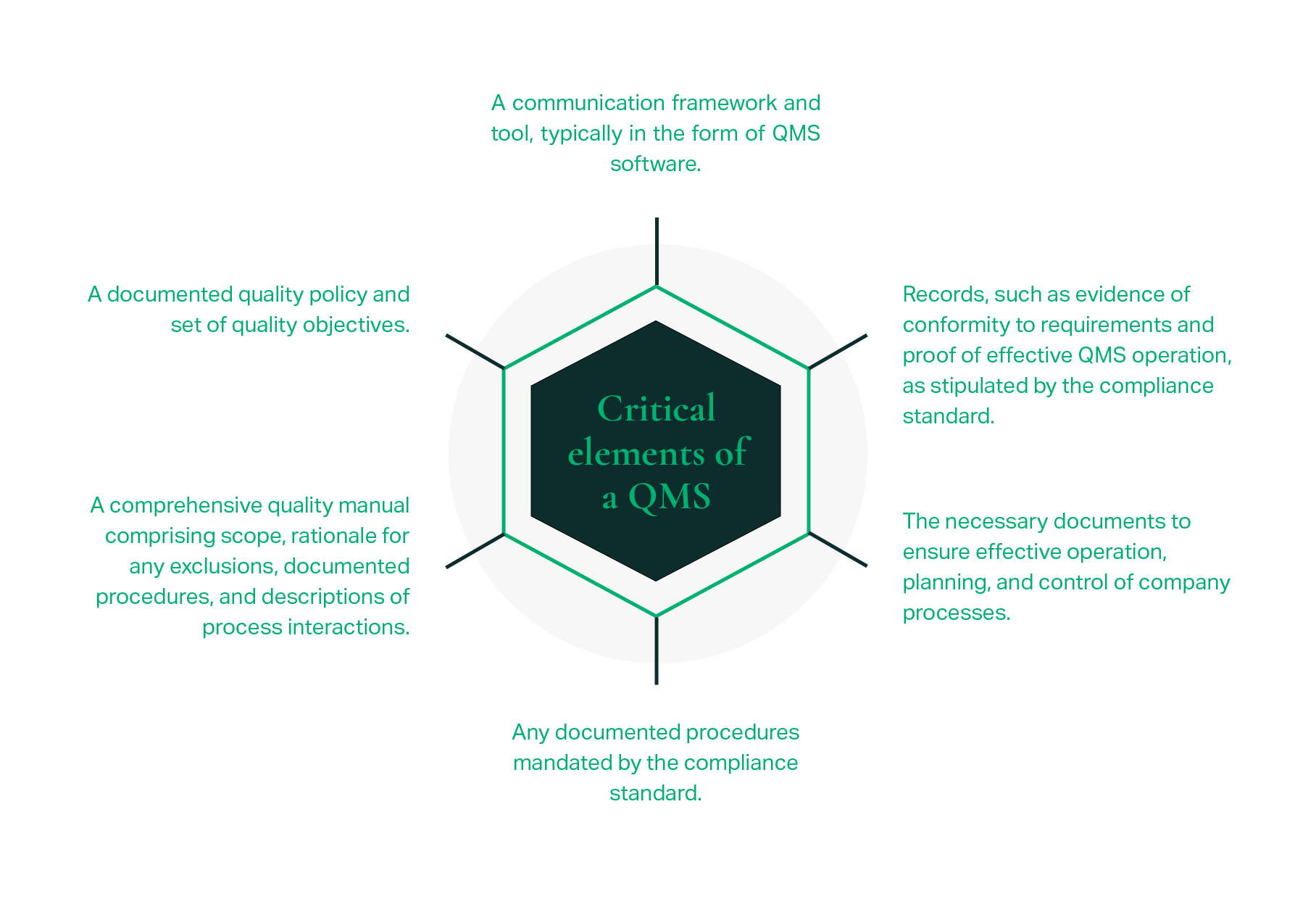 Effective organization is paramount for controlled documents, with a suggested hierarchy including the Quality Manual, Policies, Procedures, Work Instructions, Lists, and Forms. Additional document types may be incorporated at a company's discretion. To implement a QMS effectively, organizations should develop general templates for all controlled documents to ensure consistent styles and formats for ease of use, evaluate existing procedures for compliance, and consider areas outside the initial scope.
Effective organization is paramount for controlled documents, with a suggested hierarchy including the Quality Manual, Policies, Procedures, Work Instructions, Lists, and Forms. Additional document types may be incorporated at a company's discretion. To implement a QMS effectively, organizations should develop general templates for all controlled documents to ensure consistent styles and formats for ease of use, evaluate existing procedures for compliance, and consider areas outside the initial scope.
They should map quality framework management processes to identify areas needing change, organize QMS documents hierarchically using process or document maps and organization charts, and draft documents considering the intended audience, potentially translating for multilingual staff. Additionally, they should manage electronic drafts systematically to ensure proper identification, retrieval, review, and tracking, subject documents to review by Subject Matter Experts for compliance and accuracy, and obtain the necessary approval level for issued documents, secure hard copies, and train staff on their use.
By adhering to these best practices, organizations can seamlessly integrate and optimize their Quality Management System, ensuring a robust framework for sustained success.







