Effective governance ensures organizations operate in the best interests of their business, stakeholders, and society. Strong governance frameworks lead to:
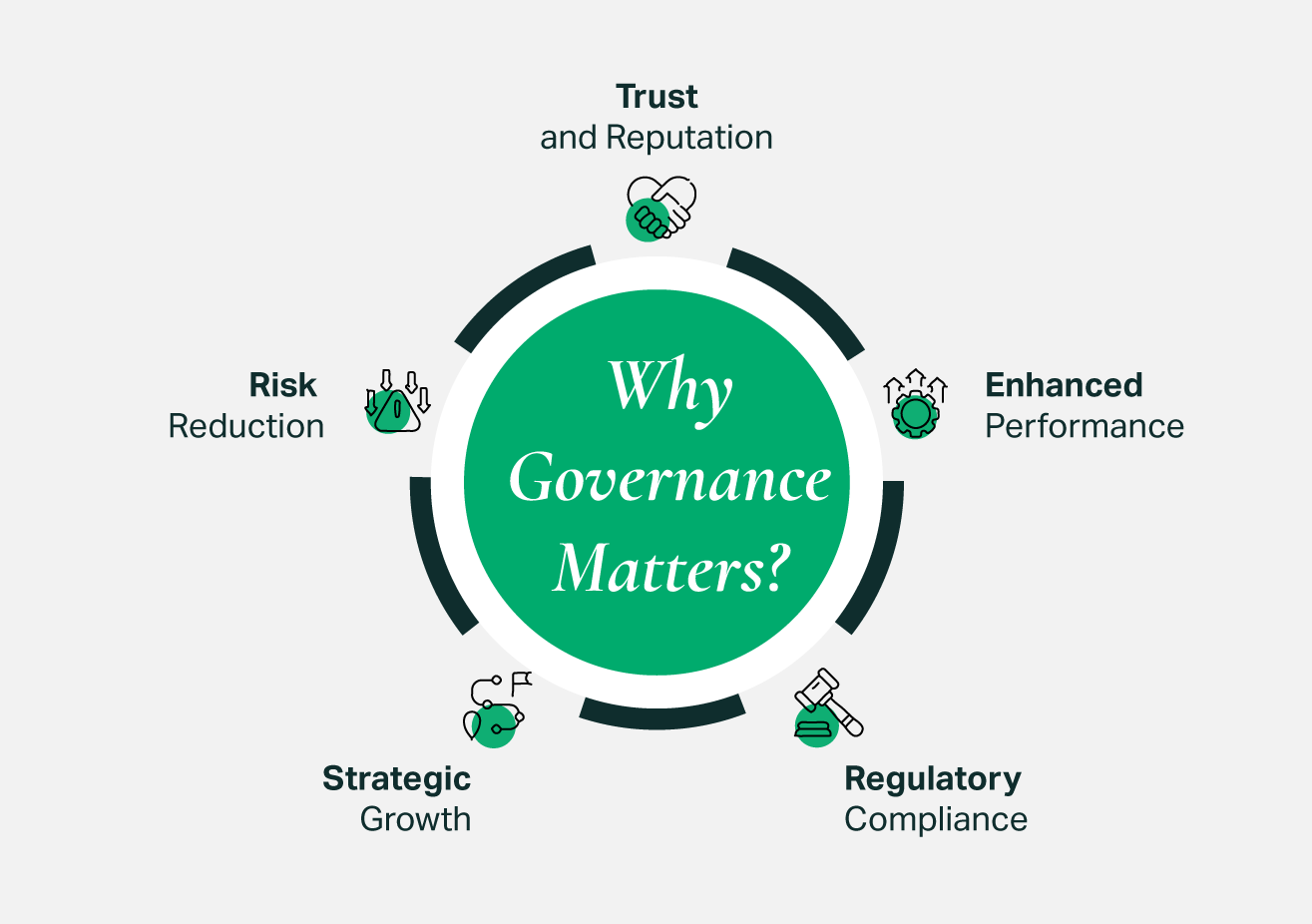
- Enhanced Performance: Stability, productivity, and long-term sustainability.
- Risk Reduction: Proactive identification and mitigation of financial, legal, and reputational risks.
- Trust and Reputation: Strengthened credibility with stakeholders, including employees, partners, customers, and regulators.
- Regulatory Compliance: Alignment with international and national laws, reducing liabilities.
- Strategic Growth: Unlocking new opportunities for expansion and innovation.
Governance has gained even greater significance with the rise of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) regulations, particularly in the European Union, where compliance is no longer optional but a strategic necessity. Organizations that align with these frameworks enhance their competitiveness and resilience in the global market.

Governance is built on eight fundamental principles, ensuring organizations operate responsibly and efficiently:
- Participation: Engaging all stakeholders in decision-making.
- Consensus-Oriented Approach: Aligning interests for balanced outcomes.
- Accountability: Ensuring transparency in responsibilities.
- Transparency: Open communication and disclosure of practices.
- Responsiveness: Adapting swiftly to changing business landscapes.
- Effectiveness & Efficiency: Maximizing resources for optimal performance.
- Equity & Inclusion: Fair treatment and equal opportunities for all.
- Rule of Law: Compliance with legal frameworks and ethical standards.
 Effective governance requires organizations to comply with regulatory frameworks, ethical standards, and industry best practices. While specific regulations may vary across regions, certain fundamental governance principles remain universal. These include:
Effective governance requires organizations to comply with regulatory frameworks, ethical standards, and industry best practices. While specific regulations may vary across regions, certain fundamental governance principles remain universal. These include:
- Risk Management & Compliance: Organizations must proactively identify risks, adhere to legal requirements, and implement industry-specific standards to ensure accountability.
- Corporate Transparency: Strong governance relies on regular audits, financial disclosures, and ethical business practices to build trust with stakeholders.
- Board Oversight & Independence: Maintaining a balanced and independent board of directors enhances decision-making and corporate integrity.
- Ethical Business Conduct: Policies against corruption, bribery, and financial misconduct safeguard organizations from reputational and legal risks.
- Workforce Development & Inclusion: Ensuring fair labor practices, diversity, and equal opportunities contributes to a sustainable and engaged workforce.
- Sustainability & Environmental Responsibility: Governance structures must integrate sustainability goals, balancing business growth with environmental and social commitments.
- Strategic Planning & Future Readiness: Organizations must continuously evaluate market trends, technological advancements, and regulatory shifts to stay resilient and competitive.
By embedding these principles into corporate governance frameworks, organizations can enhance stability, ensure regulatory compliance, and create long-term value in an evolving global landscape.
In a world marked by intense competition, uncertainties, and resource constraints, governance serves as the foundation that enables organizations to adapt, grow, and remain competitive. As businesses pursue sustainability and digital transformation, a robust governance framework ensures compliance, mitigates risks, and unlocks the potential of innovation and AI-driven efficiencies. By embedding governance into the organizational culture, companies not only avoid strategic and ethical pitfalls but also build a clear roadmap for long-term success, stakeholder trust, and meaningful global impact.